Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate virtually all chemical reactions within cells. Today, naturally found enzymes are widely used for applications like producing foods, drugs, and biofuels. However, natural enzymes are often unstable under industrial conditions, and they may not even exist for many specific reactions of interest.
In our research group, we study “enzyme catalysis”, where enzymes or whole cells are engineered by chemistry approaches to improve their stability and reaction scope. Our approaches are enzyme immobilization and enzyme modification, which makes enzymes stable, recyclable, and even with new reactivity. Eventually, these engineered enzymes will be useful for future industries, contributing to a zero-pollution and sustainable society.
Our research philosophy is the customized design – each type of enzymes is different, and thus, their engineering is customized depending on their properties and application conditions.
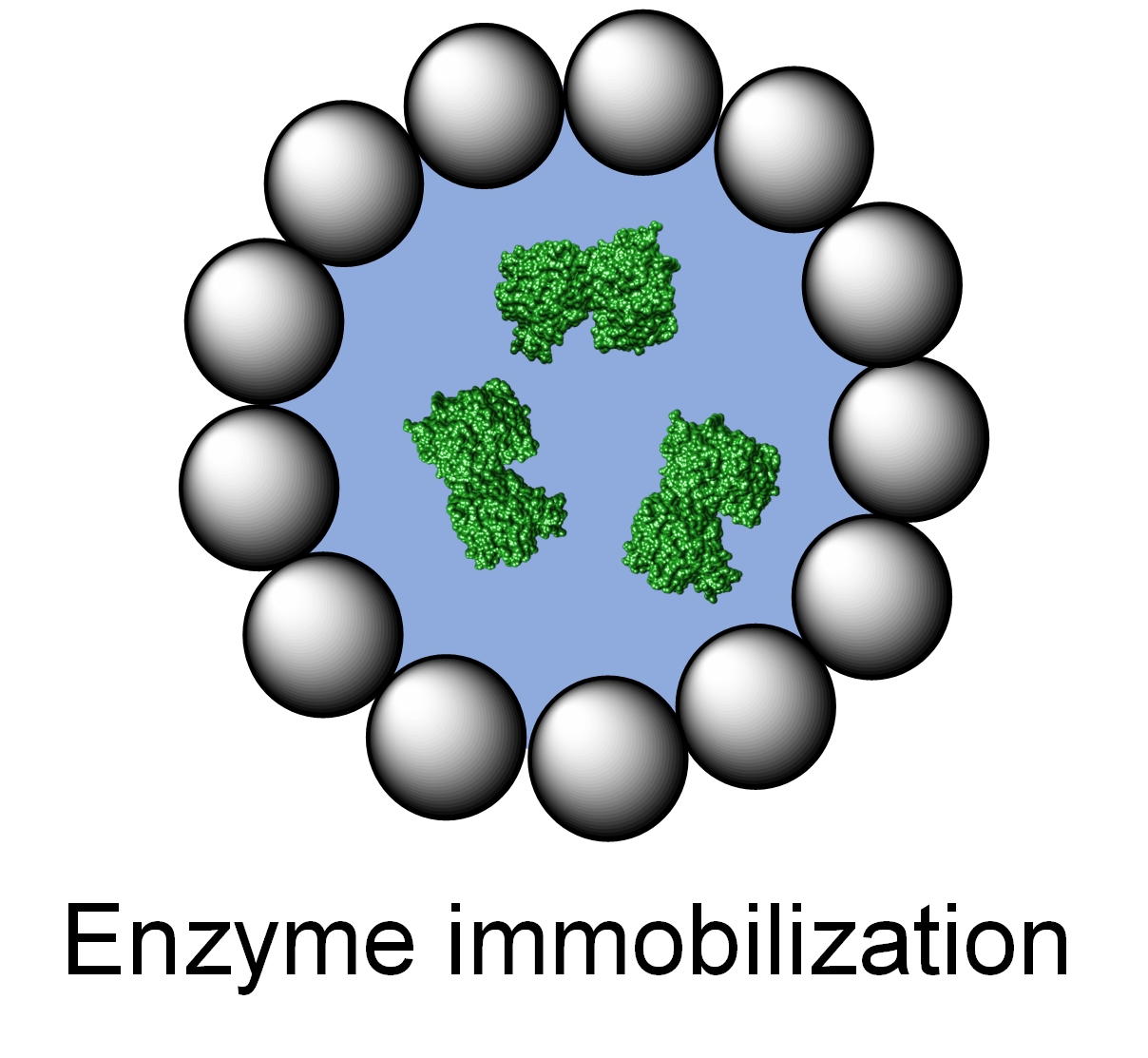
As to enzyme immobilization, we design the tailored materials/systems (rather than using as-synthesized ones) deliberately to suit enzymes best under their specific application conditions, e.g., in organic solvents. In particular, we create novel types of emulsions to encapsulate enzymes for not only high-efficiency enzymes but also their ready separability. For example, we explore Pickering emulsions and polymeric emulsions that are customized to encapsulate diverse enzymes, from stable to unstable enzymes, to address synthetic challenges from single-step to cascade reactions. In addition, we also tailor solid materials, e.g., MOF and hydrogels, to transfer enzymes from water to organic reactions media.
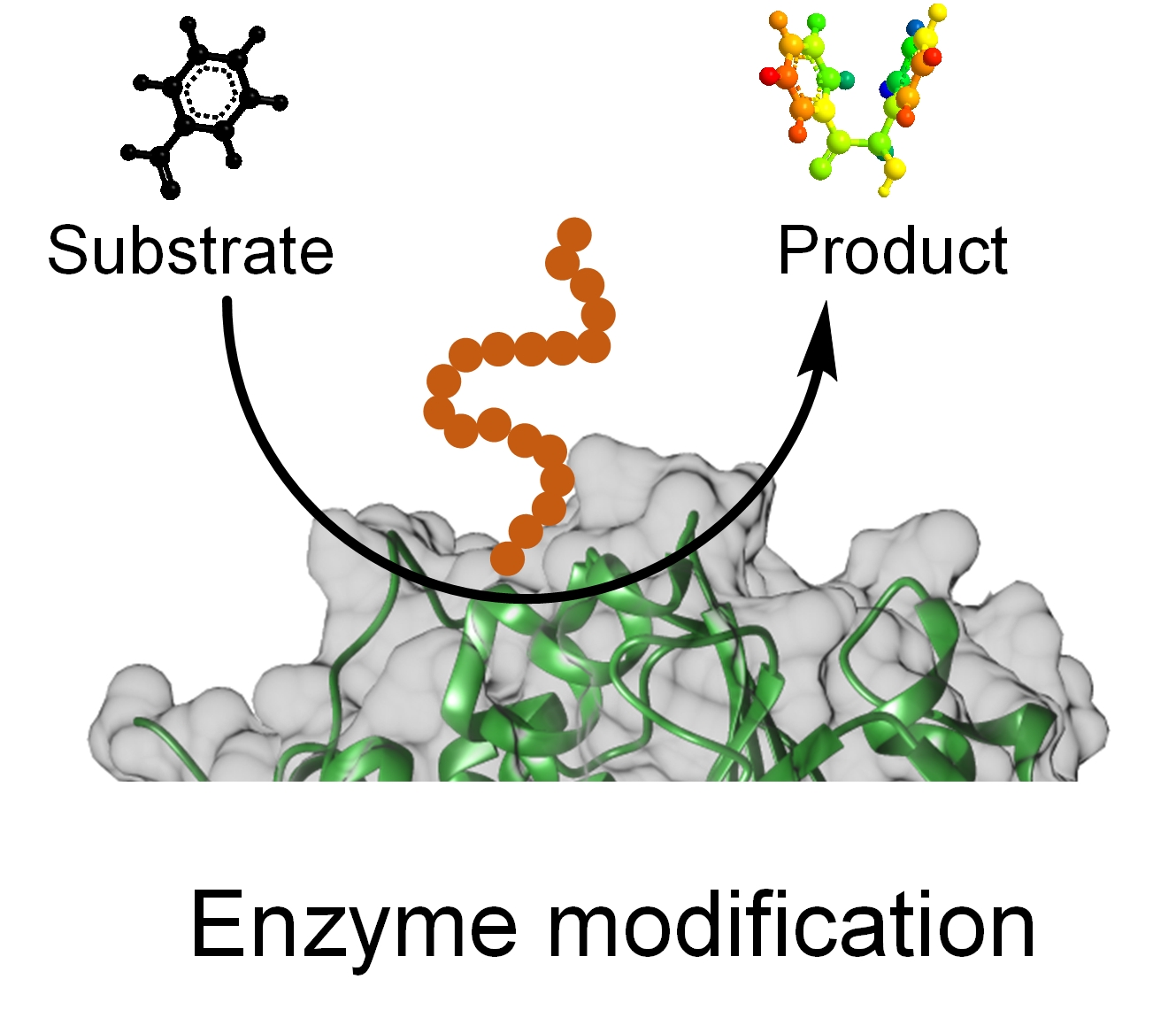
Recently, our research is largely extended to enzyme modification. Our expertise in this field is to improve enzyme catalysis by conjugating enzymes with functional and active chemicals, e.g., polymers, supramolecules, and active metals. Their modification to enzymes is expected to give enzymes new-to-nature properties that parent enzymes don’t have. For example, the combination of enzymes with polymers can enable their better stability while active species on enzymes are used for synergistic cascade reactions.
Funding

